RRSP vs. TFSA: Which Is Right for Your Retirement?
Introduction
When it comes to saving for retirement, Canadians have two powerful tools at their disposal: RRSPs and TFSAs. They have distinct advantages of their own and certainly have a place in helping you maintain sound financial security. This article will explore what RRSPs and TFSAs are, how they differ, and how to use them to meet your retirement objectives. So, read on to decide which option might be best for you.
Understanding RRSPs
1) What is an RRSP?
RRSP stands for “Registered Retirement Savings Plan,” a plan that encourages savings before or during the payment of income taxes specifically for your time after retirement. That’s because contributions you put into an RRSP are tax-deductible, reducing your taxable income until you withdraw them (in retirement).
2) Contribution Limits
The Canadian Government has a set RRSP contribution limit per year. As of 2022, the percentage limit is 18% of your prior-year earned income up until a listed ceiling; as your income climbs, the amount towards which you can apply contributions is accordingly.
3) Tax Deferral
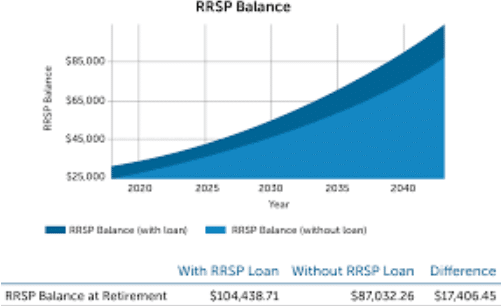
The most significant benefit of an RRSP is that you get to defer taxes. There’s no tax to pay on any capital gains or interest earned inside an RRSP when you file. However, if you take money out after age 71 and still hold the account (other than to convert to a registered retirement income fund), those earnings will eventually be subject.
The Benefits of TFSAs
What is a TFSA?
In Canada, another tax-sheltered savings vehicle is a Tax-Free Savings Account or TFSA for short. In contrast to RRSPs, the money put in TFSA is always kept from taxes. (But then — we’ll come to the real benefit of the cash-out process in a moment).
Tax-Free Growth
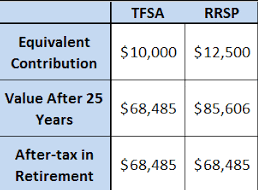
Your earnings from investments in a TFSA are entirely exempt from tax. This means all the income earned inside the account (capital gains, dividends, and interest) will be tax-free.
No Age Limit
While you are limited in your contributions to an RRSP after the “magic” number of 71, that does not apply to TFSAs: you can contribute at any point. You get to continue investing and build up your savings for the rest of your life.
Choosing Between RRSP and TFSA
Income Level Considerations
The amount you earn may dictate the type of account you need. Since contributions are tax-deductible at the source for those with an income high enough, typically, those having an upper-middle or high income will benefit more from an RRSP.
Short-Term vs. Long-Term Goals
Consider your financial goals. For people who think they will need to tap into those monies within this time horizon for something big (or an emergency), having the freedom of a TFSA might be favorable.
Retirement Income Planning
Consider the tax implications of RRSP and TFSA withdrawals in your retirement income plan. It’s equally important to balance the tax implications.
Diversification
You can utilize RRSPs and TFS as part of your retirement plan. It also offers some tax advantages and alternative sources of retirement cash flows.
Tax Considerations
Taxation of RRSP Withdrawals
In other words, when you take money from an RRSP as cash, you pay taxes on the amount withdrawn. Remember to set aside funds for all the income tax you must pay when you remove this money in retirement.
TFSA Withdrawals
Since TFSA withdrawals aren’t taxed, you don’t have to worry about them reducing your taxable income. This can be beneficial if you seek to stay in the lower tax bracket upon retiring.
Conclusion
There will always be a better answer in the RRSP vs. the TFSA debate because we all have different circumstances and attitudes towards risk. It’s just about what financial circumstances/ objectives/ inclinations work best for you). Talk with a financial adviser to develop a personalized retirement savings plan in Canada.
About hay2brick
Discover Hay2Brick:
Your Trusted Canadian Real Estate Investment Partner. We specialize in multi-family properties across the USA, leveraging 15+ years of expertise for strong cash flow and appreciation. Explore secure, profitable opportunities with our seasoned team.
